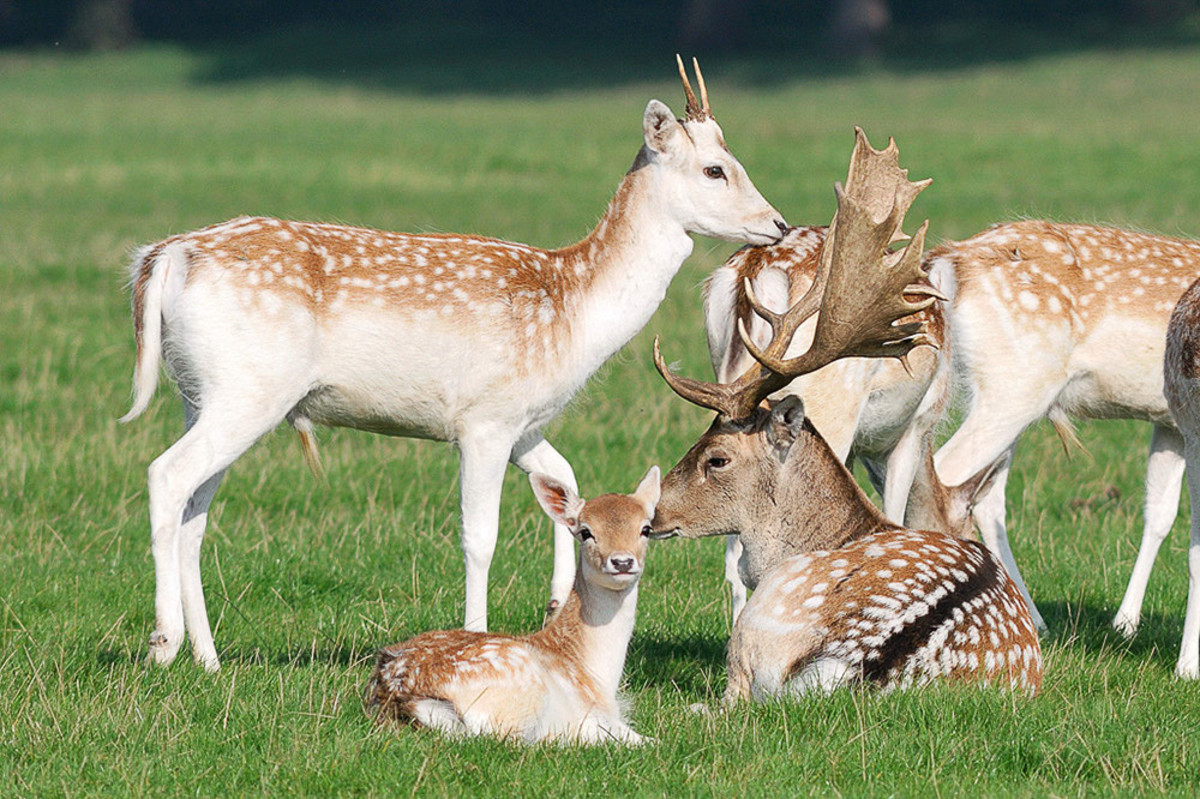
Fallow deer, with their graceful forms and dappled coats, have captured the hearts of nature enthusiasts for centuries. As pets, they offer a unique and rewarding experience, but it’s essential to understand their specific needs and requirements. Dive into this comprehensive guide to explore the fascinating world of fallow deer as pets.
From their origins and suitability as companions to their care, health, and behavior, this article provides a comprehensive overview of these enchanting animals. Whether you’re considering welcoming a fallow deer into your life or simply want to learn more about their captivating nature, this guide will illuminate your path.
Overview of Fallow Deer

Fallow deer are medium-sized deer species native to Europe and parts of Asia. They have a distinctive appearance with spotted coats, which vary in color from reddish-brown to almost white. Fallow deer are highly adaptable and can thrive in various habitats, including forests, woodlands, and grasslands.
They are known for their grazing behavior and social nature, forming herds of up to 100 individuals.
History and Origins of Fallow Deer as Pets
Fallow deer have been kept as pets for centuries, particularly in Europe and Asia. Their docile nature and striking appearance made them popular among nobility and wealthy individuals. In the 19th century, fallow deer were introduced to North America and New Zealand, where they have established feral populations.
Today, fallow deer are still popular as pets in some regions, although their ownership may be subject to regulations and permits.
Suitability as Pets
Fallow deer, with their graceful presence and gentle nature, have captivated many hearts. While their charm is undeniable, it’s crucial to carefully consider the responsibilities and challenges involved before bringing one into your life.Fallow deer require extensive space, a varied diet, and specialized care, which can be demanding for owners.
Additionally, legal and ethical concerns vary by region, and it’s essential to ensure that owning a fallow deer is permitted and meets animal welfare standards.
Space Requirements
Fallow deer need ample space to roam and graze. A minimum of 10 acres is recommended for a small herd, with additional acreage for larger groups. The enclosure should provide shelter, grazing areas, and water sources. Fencing must be sturdy and at least 8 feet high to prevent escapes.
Dietary Needs
Fallow deer are herbivores with a diverse diet. They require a balance of grasses, legumes, shrubs, and leafy greens. Hay, grain, and mineral supplements may also be necessary to ensure proper nutrition. Owners should consult with a veterinarian or experienced deer specialist to develop a tailored feeding plan.
Lifespan
Fallow deer typically live for 10-15 years in captivity. Proper care and nutrition can extend their lifespan. However, they are susceptible to various health issues, including parasites, respiratory infections, and hoof problems. Regular veterinary checkups are essential for maintaining their well-being.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
The legality of owning fallow deer varies by state and country. In some areas, they are considered exotic animals and require special permits or licenses. Owners must comply with local ordinances and ensure their animals are well-cared for. Ethical considerations also come into play, as fallow deer are wild animals and may not be suitable for domestication in all situations.Ultimately,
the decision of whether or not to keep fallow deer as pets is a complex one that requires careful consideration of their needs and the responsibilities involved. While they can bring joy and companionship, owners must be prepared to provide a suitable environment and care for these beautiful creatures throughout their lives.
Care and Maintenance: Fallow Deer As Pets

Fallow deer require specialized care and attention to thrive in captivity. Providing them with a suitable habitat, proper nutrition, and regular veterinary care is crucial for their well-being.
Housing
Fallow deer need ample space to roam and graze. An enclosure of at least 5 acres is recommended, with fencing that is at least 8 feet tall. The enclosure should provide shelter from the elements, such as a barn or lean-to, as well as access to fresh water and shade.
Feeding
Fallow deer are herbivores and their diet consists primarily of grasses, leaves, and twigs. They should be provided with a variety of high-quality hay, such as alfalfa or orchard grass, as well as fresh fruits and vegetables. It is important to ensure that they have access to a constant supply of fresh water.
Veterinary Care, Fallow deer as pets
Regular veterinary care is essential for fallow deer. They should be vaccinated against common diseases, such as tetanus and rabies, and receive regular checkups to monitor their health and prevent any potential health issues.
Socialization and Enrichment
Fallow deer are social animals and they require interaction with other deer to thrive. They should be kept in pairs or small groups, and they should be provided with enrichment activities, such as toys, puzzles, and interactive feeders, to stimulate their minds and prevent boredom.
Handling and Training
Fallow deer can be trained to be handled and led, but they require patience and positive reinforcement. They are not typically aggressive animals, but they can be startled or defensive if they feel threatened. It is important to approach them calmly and slowly, and to avoid making sudden movements.
Health and Behavior

Fallow deer are generally healthy animals, but like all species, they are susceptible to certain health issues and diseases. Some of the most common health problems in fallow deer include:
-
-*Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD)
CWD is a fatal neurological disease that affects deer, elk, and moose. It is caused by a prion, which is a type of infectious protein. CWD can cause a variety of symptoms, including weight loss, loss of coordination, and behavioral changes.
There is no cure for CWD, and it is always fatal.
-*Footrot
Footrot is a bacterial infection that affects the hooves of deer. It can cause lameness, pain, and swelling. Footrot is treated with antibiotics.
-*Pneumonia
Fallow deer can make interesting pets, but if you’re looking for a more unique way to remember your fallow deer, you might consider deer skull cap mount kits . These kits allow you to preserve and display the skull of your fallow deer, creating a lasting memento of your pet.
The process is relatively simple and can be a great way to learn more about the anatomy of deer.
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that can be caused by bacteria or viruses. It can cause coughing, difficulty breathing, and fever. Pneumonia is treated with antibiotics.
-*Gastrointestinal parasites
Gastrointestinal parasites are common in deer. They can cause diarrhea, weight loss, and poor growth. Gastrointestinal parasites are treated with antiparasitic medication.
In addition to these health issues, fallow deer can also suffer from stress and illness. Signs of stress in fallow deer include:
-
-*Pacing
Pacing is a sign of stress in fallow deer. They may pace back and forth in their enclosure or around their food.
-*Head bobbing
Head bobbing is another sign of stress in fallow deer. They may bob their heads up and down or side to side.
-*Lip licking
Lip licking is a sign of stress or anxiety in fallow deer. They may lick their lips repeatedly or excessively.
-*Tail flicking
Tail flicking is a sign of stress or irritation in fallow deer. They may flick their tails back and forth or side to side.
-*Aggression
Aggression is a sign of stress or illness in fallow deer. They may become aggressive towards other deer or towards humans.
If you notice any of these signs of stress or illness in your fallow deer, it is important to contact your veterinarian immediately.The lifespan of fallow deer in captivity is typically 10-15 years. However, some fallow deer have been known to live for up to 20 years.
The mortality rate of fallow deer in captivity is relatively low, but it can vary depending on the age and health of the deer.
Fallow deer can make great pets, but they can also be a hazard on the road. As reported in bmw hits deer on autobahn , a BMW driver recently hit a deer on the Autobahn, causing extensive damage to the car.
While fallow deer are generally gentle creatures, they can be unpredictable when startled, so it’s important to be aware of your surroundings when driving in areas where they are known to live. However, with proper care and attention, fallow deer can make wonderful companions.
Alternative Options

While keeping fallow deer as pets may not be the most suitable option, there are numerous alternative ways to interact with and appreciate these majestic creatures.
Observing fallow deer in their natural habitats offers a unique and enriching experience. Their elegant movements, graceful grazing, and social interactions are fascinating to witness.
Wildlife Sanctuaries
Visiting wildlife sanctuaries or parks that house fallow deer provides an opportunity to observe them up close without disturbing their natural behaviors. These sanctuaries often offer guided tours and educational programs that enhance the experience.
Conservation Efforts
Participating in conservation efforts focused on fallow deer is a meaningful way to contribute to their well-being. Volunteering with organizations involved in habitat restoration, research, or anti-poaching initiatives allows individuals to make a positive impact on the species’ survival.
Resources for Fallow Deer Conservation
- Wildlife Conservation Society: https://www.wcs.org/
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN): https://www.iucn.org/
- The Wildlife Trusts: https://www.wildlifetrusts.org/
Ending Remarks
Fallow deer as pets present a unique blend of challenges and rewards. Their captivating beauty, gentle nature, and social instincts make them cherished companions. However, their specific dietary needs, spacious habitat requirements, and potential health concerns necessitate responsible and dedicated ownership.
By understanding their needs and providing them with the utmost care, you can create a fulfilling and enriching life for these majestic creatures.
Essential FAQs
Are fallow deer easy to care for as pets?
While fallow deer can be affectionate and rewarding companions, they require specialized care. Their diet, housing, and healthcare needs must be met diligently to ensure their well-being.
What is the lifespan of a fallow deer in captivity?
With proper care, fallow deer can live for up to 15 years in captivity.
Can fallow deer be kept as indoor pets?
No, fallow deer require ample outdoor space to roam and socialize. They are not suitable for indoor living.